JEE Exam > JEE Questions > NiCl2 {P(C2H5)2(C6H5)}2 exhibits temperature ...
Start Learning for Free
NiCl2 {P(C2H5)2(C6H5)}2 exhibits temperature depend-ent magnetic behaviour (paramagnetic/diamagnetic). The coordination geometries of Ni2+ in the paramagnetic and diamagnetic states are respectively
- a)tetrahedral and tetrahedral
- b)square planar and square planar
- c)tetrahedral and square planar
- d)square planar and tetrahedral
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
NiCl2 {P(C2H5)2(C6H5)}2 exhibits temperature depend-ent magnetic behav...
In both states (paramagnetic and diamagnetic) of the given complex, Ni exists as Ni2+ whose electronic configuration is [Ar] 3d84s0.
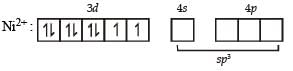
In the above paramagnetic state the geometry of the complex is sp3 giving tetrahedral geometry.
The diamagnetic state is achieved by pairing of electrons in 3d orbital.

Thus the geometry of the complex will be dsp2 giving square planar geometry.
Most Upvoted Answer
NiCl2 {P(C2H5)2(C6H5)}2 exhibits temperature depend-ent magnetic behav...
Coordination Geometry of NiCl2 {P(C2H5)2(C6H5)}2
In order to determine the coordination geometry of Ni2+ in NiCl2 {P(C2H5)2(C6H5)}2, we need to analyze the structure and electronic configuration of the complex.
Structure of the complex:
The complex consists of a central nickel ion (Ni2+) surrounded by ligands. The ligands in this case are two chloride ions (Cl-) and two bidentate ligands, P(C2H5)2(C6H5). The ligands form coordination bonds with the central metal ion through their lone pairs of electrons.
Electronic configuration of Ni2+:
The electronic configuration of Ni2+ is [Ar] 3d8. In this configuration, there are eight electrons in the d orbital. According to Hund's rule, these electrons will occupy different d orbitals before pairing up, resulting in unpaired electrons.
Temperature-dependent magnetic behavior:
In paramagnetic substances, the presence of unpaired electrons leads to the alignment of the spins of these electrons in the presence of a magnetic field. This alignment results in a net magnetic moment, causing the substance to be attracted to a magnetic field. On the other hand, diamagnetic substances have no unpaired electrons and are not attracted to a magnetic field.
Coordination geometry in the paramagnetic state:
In the paramagnetic state, the complex exhibits temperature-dependent magnetic behavior due to the presence of unpaired electrons. The coordination geometry of Ni2+ in the paramagnetic state is tetrahedral.
Explanation:
The tetrahedral coordination geometry is observed when the ligands around the central metal ion are arranged in a tetrahedral shape. In the case of NiCl2 {P(C2H5)2(C6H5)}2, the two chloride ions and two bidentate ligands (P(C2H5)2(C6H5)) form a tetrahedral arrangement around the Ni2+ ion.
Coordination geometry in the diamagnetic state:
In the diamagnetic state, the complex does not exhibit temperature-dependent magnetic behavior due to the absence of unpaired electrons. The coordination geometry of Ni2+ in the diamagnetic state is square planar.
Explanation:
The square planar coordination geometry is observed when the ligands around the central metal ion are arranged in a square planar shape. In the absence of unpaired electrons, the ligands form a square planar arrangement around the Ni2+ ion.
Conclusion:
In NiCl2 {P(C2H5)2(C6H5)}2, the coordination geometry of Ni2+ in the paramagnetic state is tetrahedral, while in the diamagnetic state, it is square planar. The presence or absence of unpaired electrons determines the magnetic behavior and, consequently, the coordination geometry of the complex.
In order to determine the coordination geometry of Ni2+ in NiCl2 {P(C2H5)2(C6H5)}2, we need to analyze the structure and electronic configuration of the complex.
Structure of the complex:
The complex consists of a central nickel ion (Ni2+) surrounded by ligands. The ligands in this case are two chloride ions (Cl-) and two bidentate ligands, P(C2H5)2(C6H5). The ligands form coordination bonds with the central metal ion through their lone pairs of electrons.
Electronic configuration of Ni2+:
The electronic configuration of Ni2+ is [Ar] 3d8. In this configuration, there are eight electrons in the d orbital. According to Hund's rule, these electrons will occupy different d orbitals before pairing up, resulting in unpaired electrons.
Temperature-dependent magnetic behavior:
In paramagnetic substances, the presence of unpaired electrons leads to the alignment of the spins of these electrons in the presence of a magnetic field. This alignment results in a net magnetic moment, causing the substance to be attracted to a magnetic field. On the other hand, diamagnetic substances have no unpaired electrons and are not attracted to a magnetic field.
Coordination geometry in the paramagnetic state:
In the paramagnetic state, the complex exhibits temperature-dependent magnetic behavior due to the presence of unpaired electrons. The coordination geometry of Ni2+ in the paramagnetic state is tetrahedral.
Explanation:
The tetrahedral coordination geometry is observed when the ligands around the central metal ion are arranged in a tetrahedral shape. In the case of NiCl2 {P(C2H5)2(C6H5)}2, the two chloride ions and two bidentate ligands (P(C2H5)2(C6H5)) form a tetrahedral arrangement around the Ni2+ ion.
Coordination geometry in the diamagnetic state:
In the diamagnetic state, the complex does not exhibit temperature-dependent magnetic behavior due to the absence of unpaired electrons. The coordination geometry of Ni2+ in the diamagnetic state is square planar.
Explanation:
The square planar coordination geometry is observed when the ligands around the central metal ion are arranged in a square planar shape. In the absence of unpaired electrons, the ligands form a square planar arrangement around the Ni2+ ion.
Conclusion:
In NiCl2 {P(C2H5)2(C6H5)}2, the coordination geometry of Ni2+ in the paramagnetic state is tetrahedral, while in the diamagnetic state, it is square planar. The presence or absence of unpaired electrons determines the magnetic behavior and, consequently, the coordination geometry of the complex.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
Question Description
NiCl2 {P(C2H5)2(C6H5)}2 exhibits temperature depend-ent magnetic behaviour (paramagnetic/diamagnetic). The coordination geometries of Ni2+ in the paramagnetic and diamagnetic states are respectivelya)tetrahedral and tetrahedralb)square planar and square planarc)tetrahedral and square planard)square planar and tetrahedralCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about NiCl2 {P(C2H5)2(C6H5)}2 exhibits temperature depend-ent magnetic behaviour (paramagnetic/diamagnetic). The coordination geometries of Ni2+ in the paramagnetic and diamagnetic states are respectivelya)tetrahedral and tetrahedralb)square planar and square planarc)tetrahedral and square planard)square planar and tetrahedralCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for NiCl2 {P(C2H5)2(C6H5)}2 exhibits temperature depend-ent magnetic behaviour (paramagnetic/diamagnetic). The coordination geometries of Ni2+ in the paramagnetic and diamagnetic states are respectivelya)tetrahedral and tetrahedralb)square planar and square planarc)tetrahedral and square planard)square planar and tetrahedralCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
NiCl2 {P(C2H5)2(C6H5)}2 exhibits temperature depend-ent magnetic behaviour (paramagnetic/diamagnetic). The coordination geometries of Ni2+ in the paramagnetic and diamagnetic states are respectivelya)tetrahedral and tetrahedralb)square planar and square planarc)tetrahedral and square planard)square planar and tetrahedralCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about NiCl2 {P(C2H5)2(C6H5)}2 exhibits temperature depend-ent magnetic behaviour (paramagnetic/diamagnetic). The coordination geometries of Ni2+ in the paramagnetic and diamagnetic states are respectivelya)tetrahedral and tetrahedralb)square planar and square planarc)tetrahedral and square planard)square planar and tetrahedralCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for NiCl2 {P(C2H5)2(C6H5)}2 exhibits temperature depend-ent magnetic behaviour (paramagnetic/diamagnetic). The coordination geometries of Ni2+ in the paramagnetic and diamagnetic states are respectivelya)tetrahedral and tetrahedralb)square planar and square planarc)tetrahedral and square planard)square planar and tetrahedralCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for NiCl2 {P(C2H5)2(C6H5)}2 exhibits temperature depend-ent magnetic behaviour (paramagnetic/diamagnetic). The coordination geometries of Ni2+ in the paramagnetic and diamagnetic states are respectivelya)tetrahedral and tetrahedralb)square planar and square planarc)tetrahedral and square planard)square planar and tetrahedralCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of NiCl2 {P(C2H5)2(C6H5)}2 exhibits temperature depend-ent magnetic behaviour (paramagnetic/diamagnetic). The coordination geometries of Ni2+ in the paramagnetic and diamagnetic states are respectivelya)tetrahedral and tetrahedralb)square planar and square planarc)tetrahedral and square planard)square planar and tetrahedralCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
NiCl2 {P(C2H5)2(C6H5)}2 exhibits temperature depend-ent magnetic behaviour (paramagnetic/diamagnetic). The coordination geometries of Ni2+ in the paramagnetic and diamagnetic states are respectivelya)tetrahedral and tetrahedralb)square planar and square planarc)tetrahedral and square planard)square planar and tetrahedralCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for NiCl2 {P(C2H5)2(C6H5)}2 exhibits temperature depend-ent magnetic behaviour (paramagnetic/diamagnetic). The coordination geometries of Ni2+ in the paramagnetic and diamagnetic states are respectivelya)tetrahedral and tetrahedralb)square planar and square planarc)tetrahedral and square planard)square planar and tetrahedralCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of NiCl2 {P(C2H5)2(C6H5)}2 exhibits temperature depend-ent magnetic behaviour (paramagnetic/diamagnetic). The coordination geometries of Ni2+ in the paramagnetic and diamagnetic states are respectivelya)tetrahedral and tetrahedralb)square planar and square planarc)tetrahedral and square planard)square planar and tetrahedralCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice NiCl2 {P(C2H5)2(C6H5)}2 exhibits temperature depend-ent magnetic behaviour (paramagnetic/diamagnetic). The coordination geometries of Ni2+ in the paramagnetic and diamagnetic states are respectivelya)tetrahedral and tetrahedralb)square planar and square planarc)tetrahedral and square planard)square planar and tetrahedralCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Signup to solve all Doubts
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.